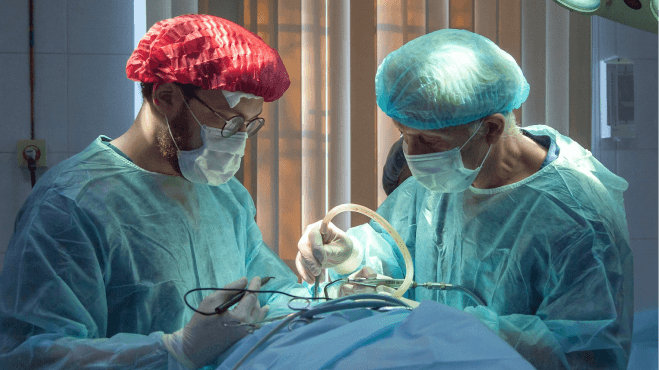
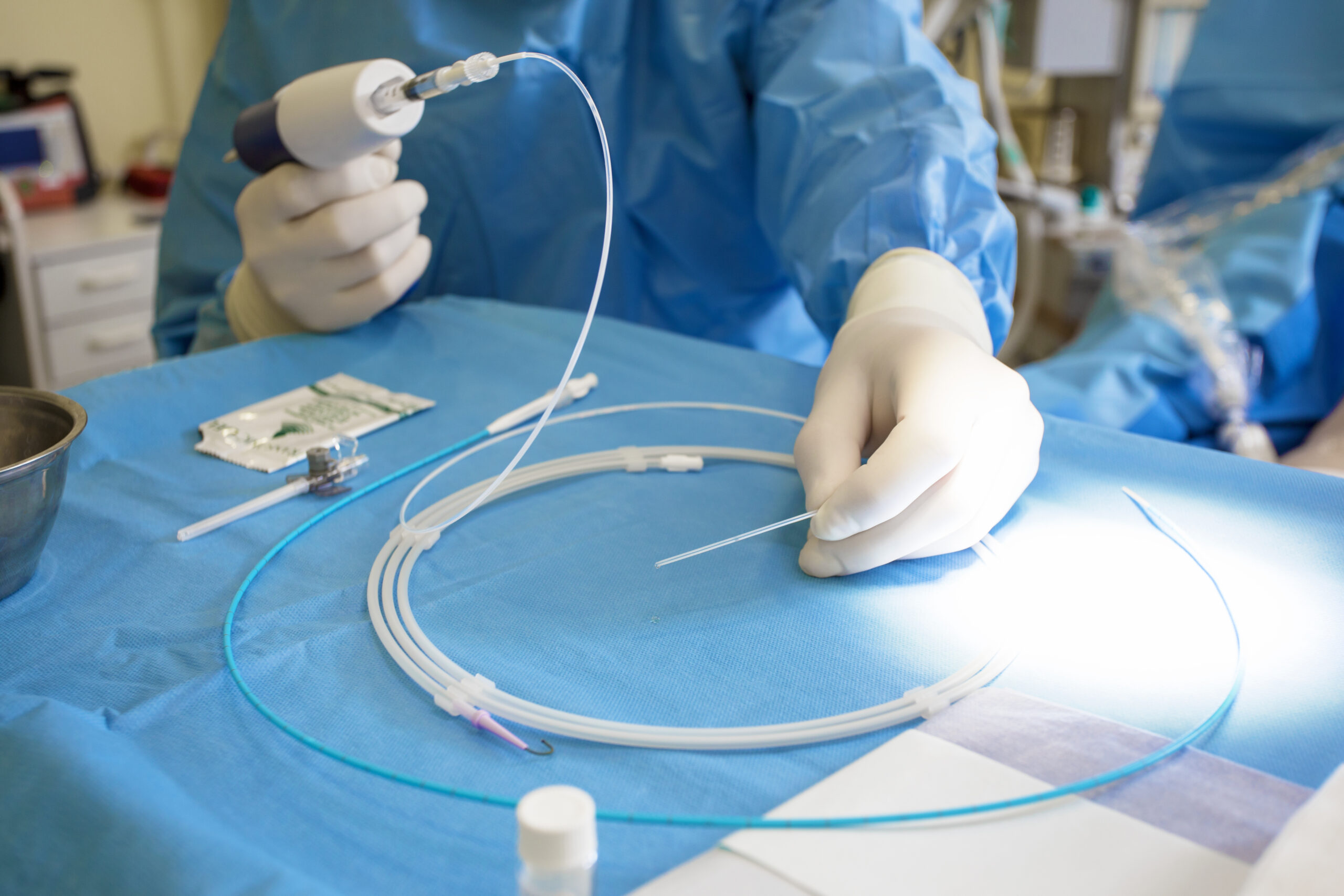
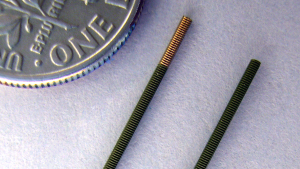
Precise MicroBlasting Technologies for Medical Applications
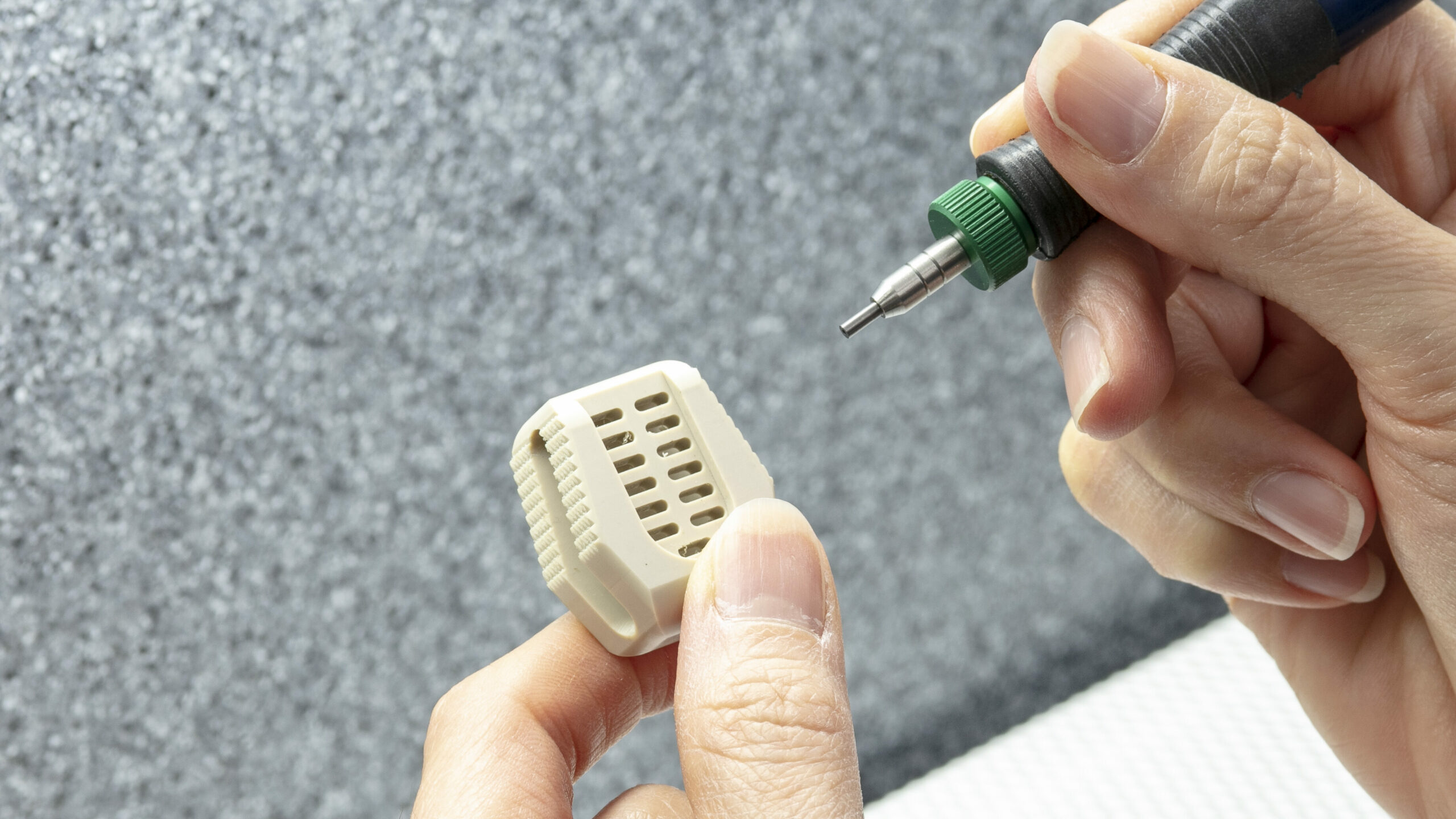
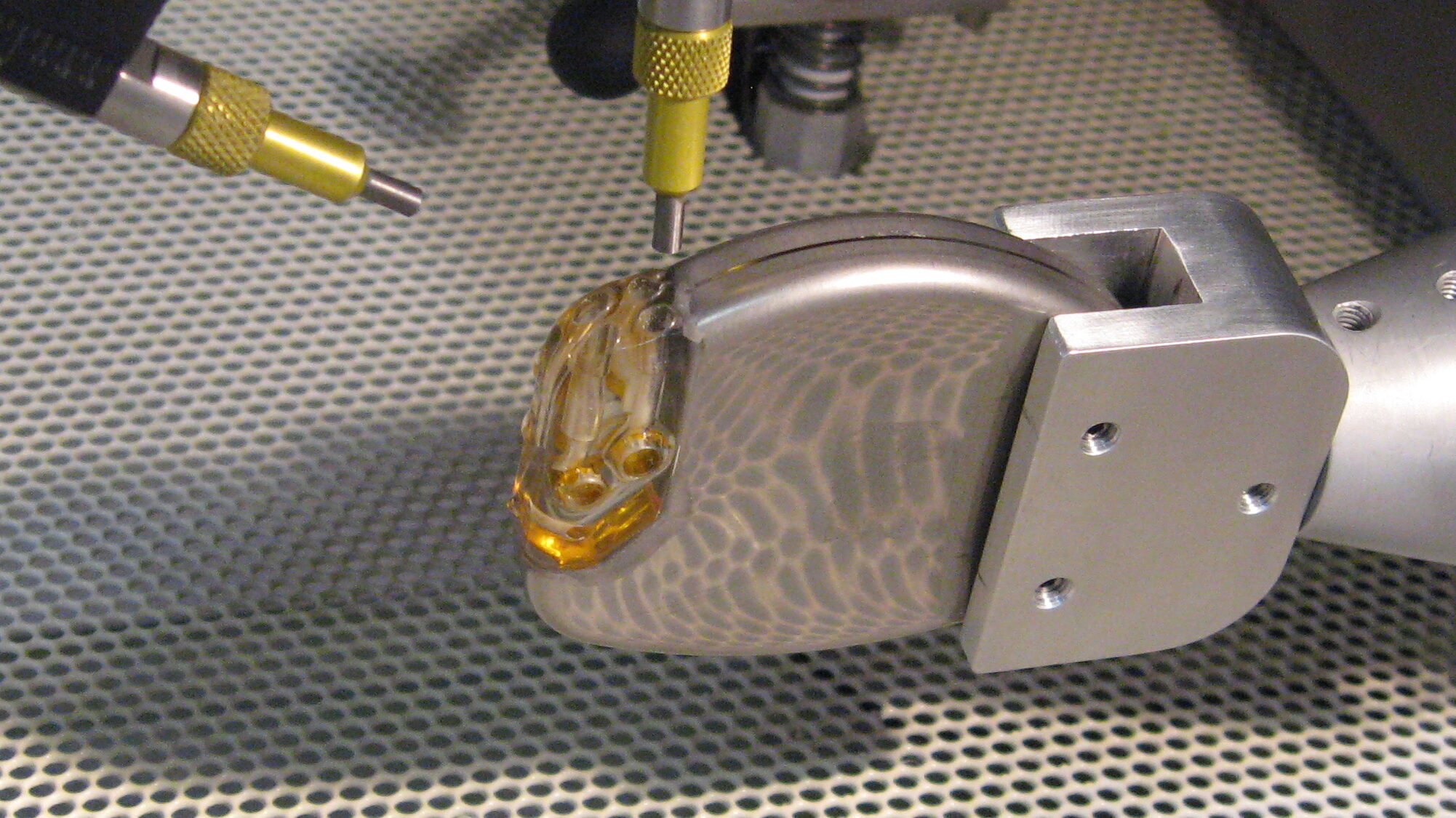
If you clean stents, deburr needles, texture implants or machine graphite from mechanical heart valves, you know the importance of control. Medical manufacturing must meet strict standards, which means medical implants and devices require a surface refinement tool that delivers pinpoint precision and repeatable results. We’ll work closely with you to land on custom solutions for your medical engineering and manufacturing needs.
Explore medical parts used in the body that have been manufactured and optimized withour microblasting systems

PEEK spinal implants
What? – Remove fine feather burrs
Why MicroBlasting? – Operators easily follow the contours of an implant to remove burrs quickly and safely without causing dimensional changes.
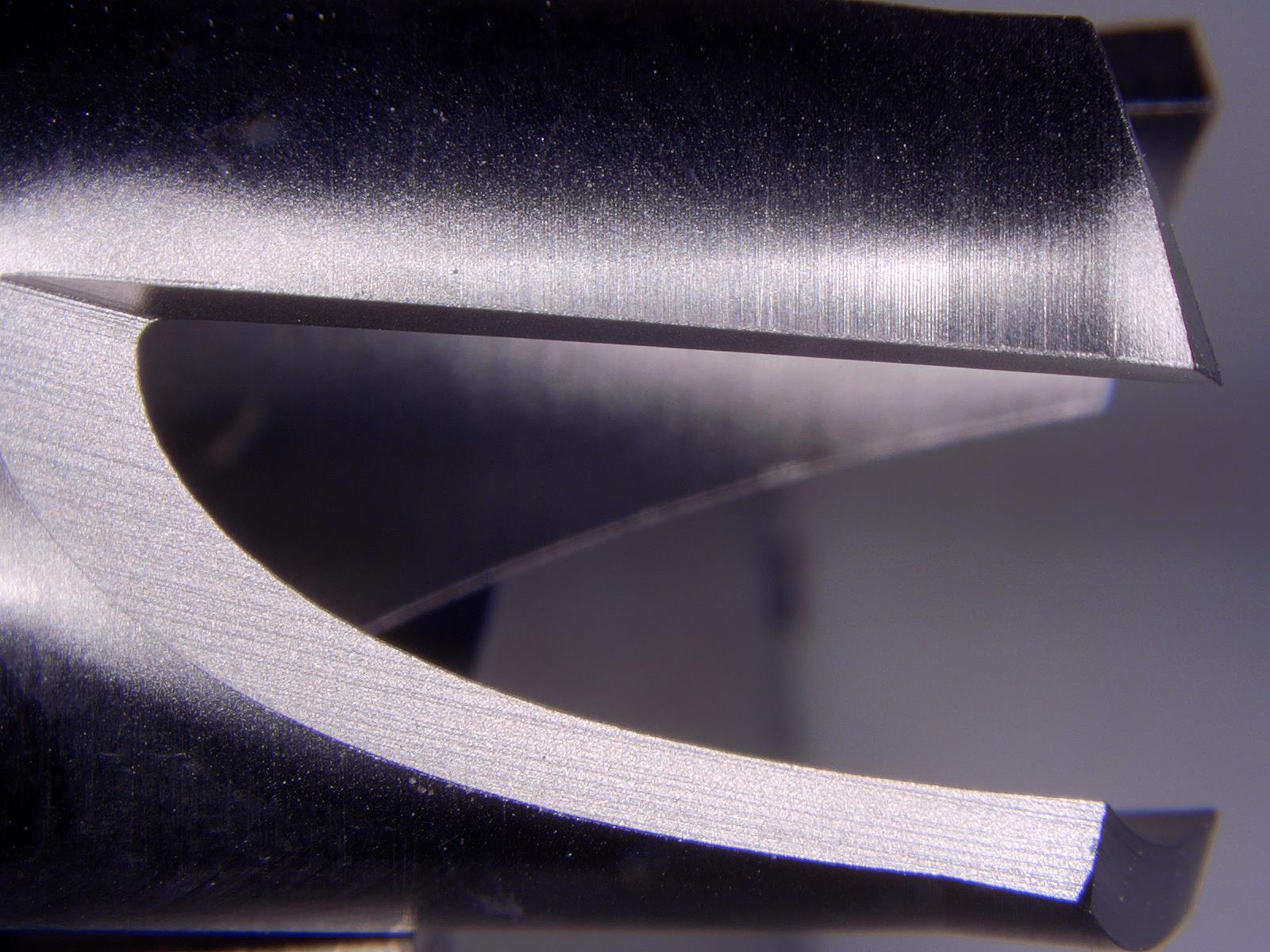
Cranial Perforator
What? Deburr blades for drilling cores out of a section in the skull
Why MicroBlasting? Removes burrs effectively without dulling the cutting edge.
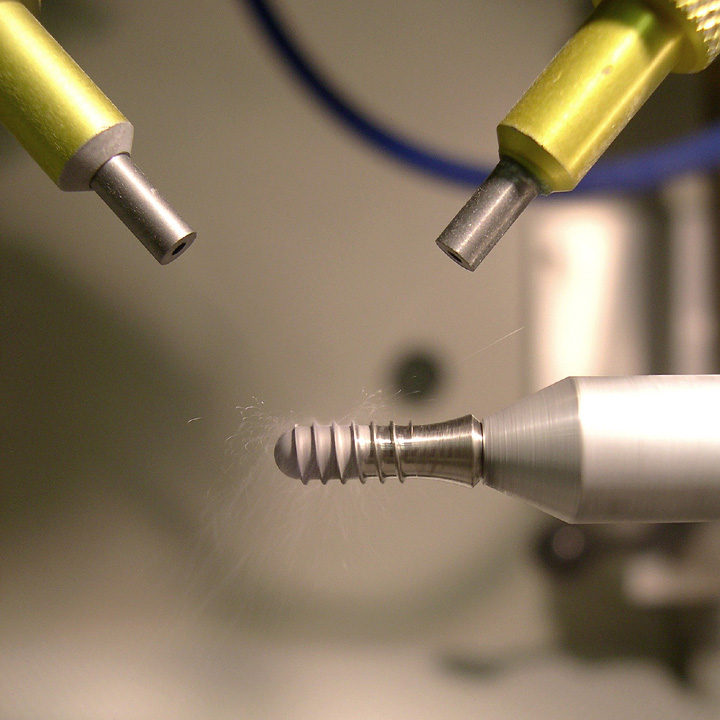
Dental Implants
What? – Create a textured surface optimized for osseointegration
Why MicroBlasting? – Achieve a consistent, specific Ra surface finish without reducing major diameter of the threads
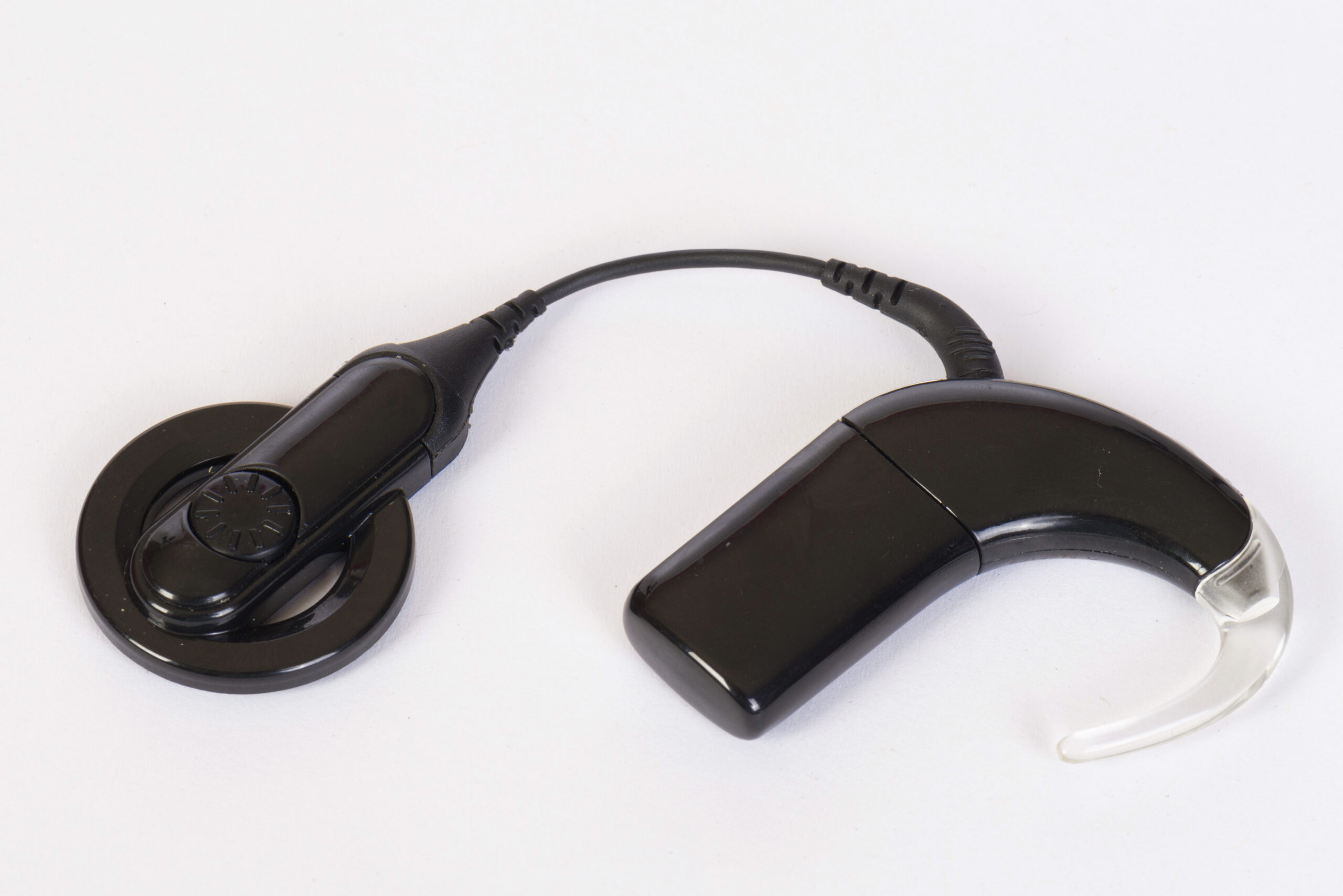

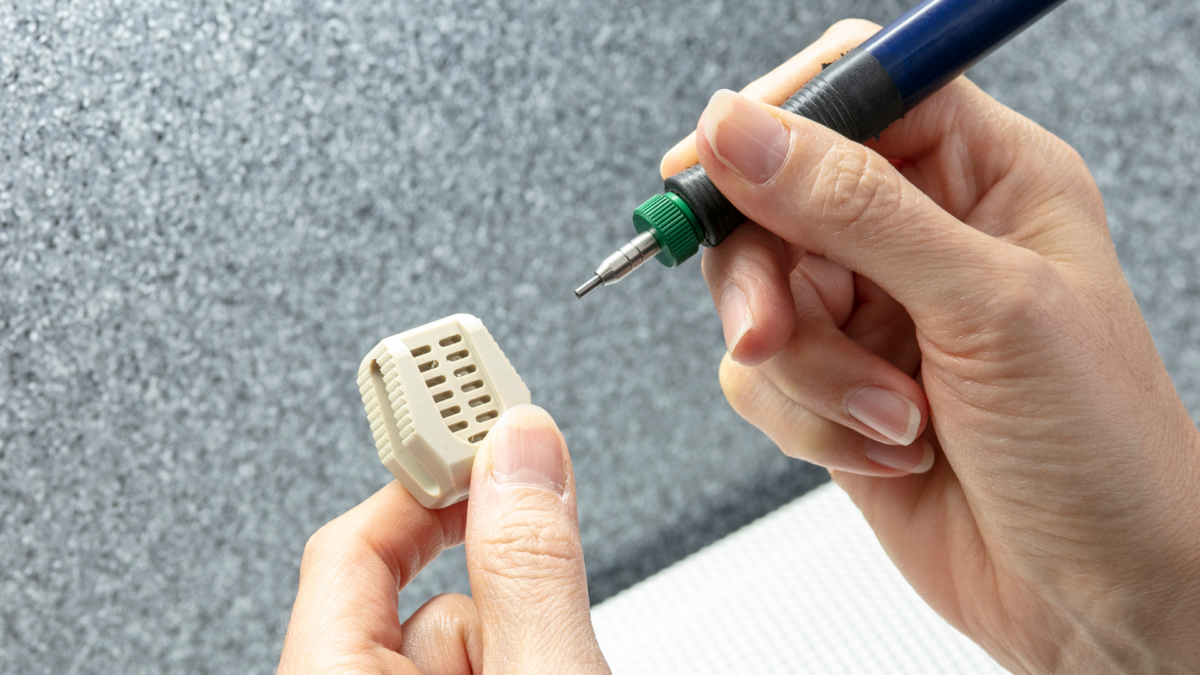
Cochlear Implants
What? Deburr miniature components
Why MicroBlasting? Safely removes burrs without causing dimensional changes
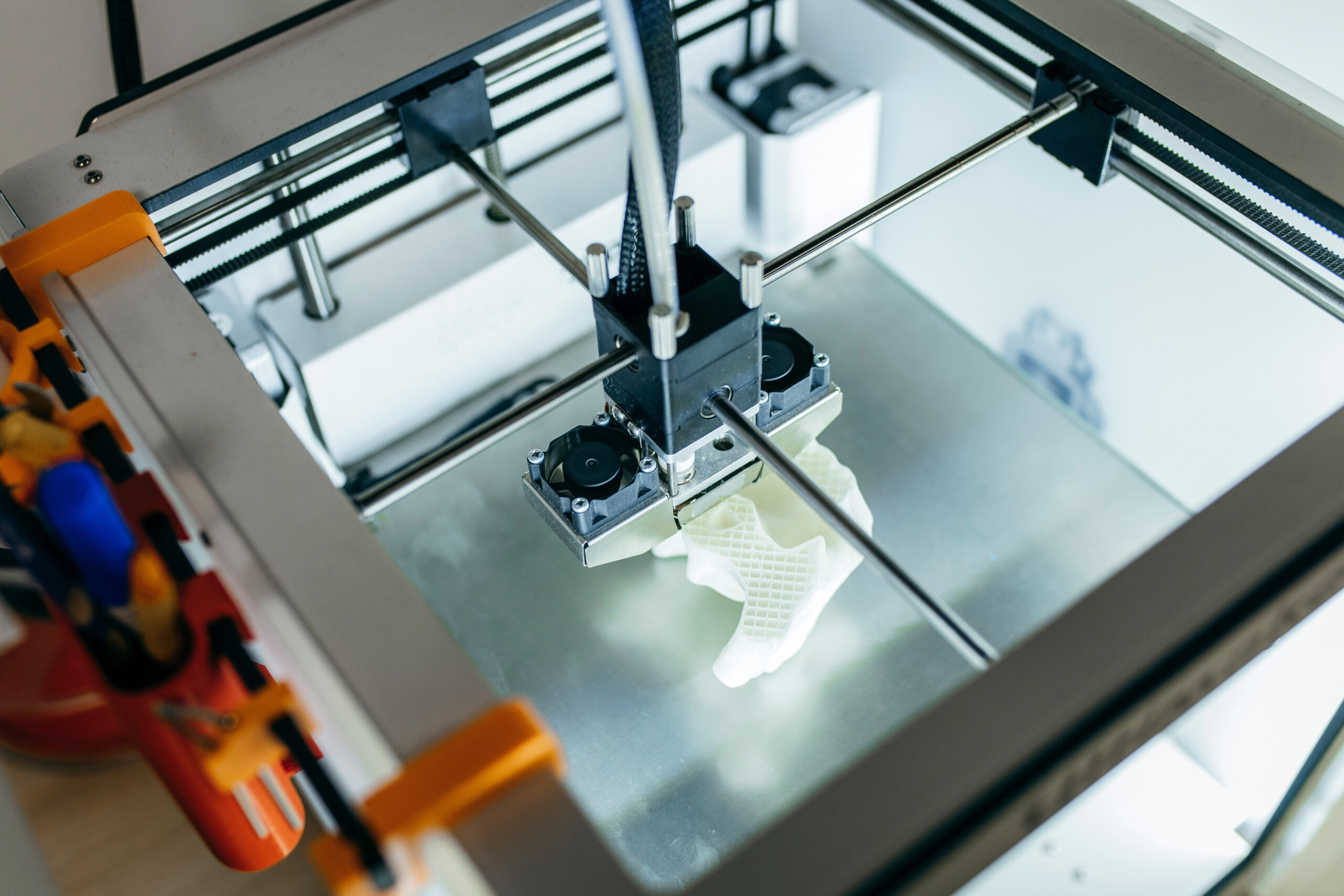

3D printed ear parts
What? Strip semi-integrated material from the surface of 3D printed components; create a uniform cosmetic finish
Why MicroBlasting? Removes material without causing dimensional changes
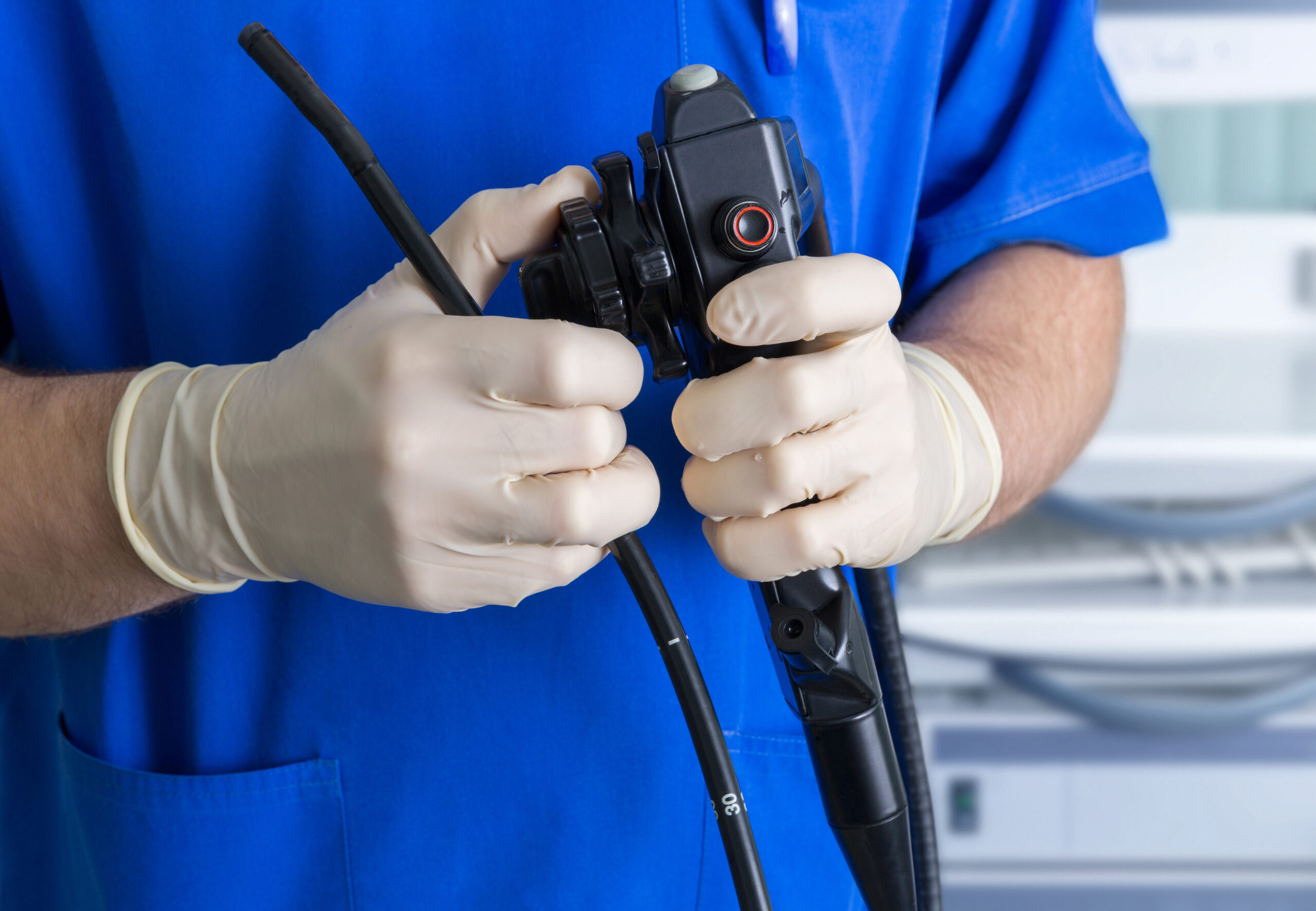
Endoscope
What? Texture for radiopacity
Why MicroBlasting? Efficiently applies a uniform surface finish
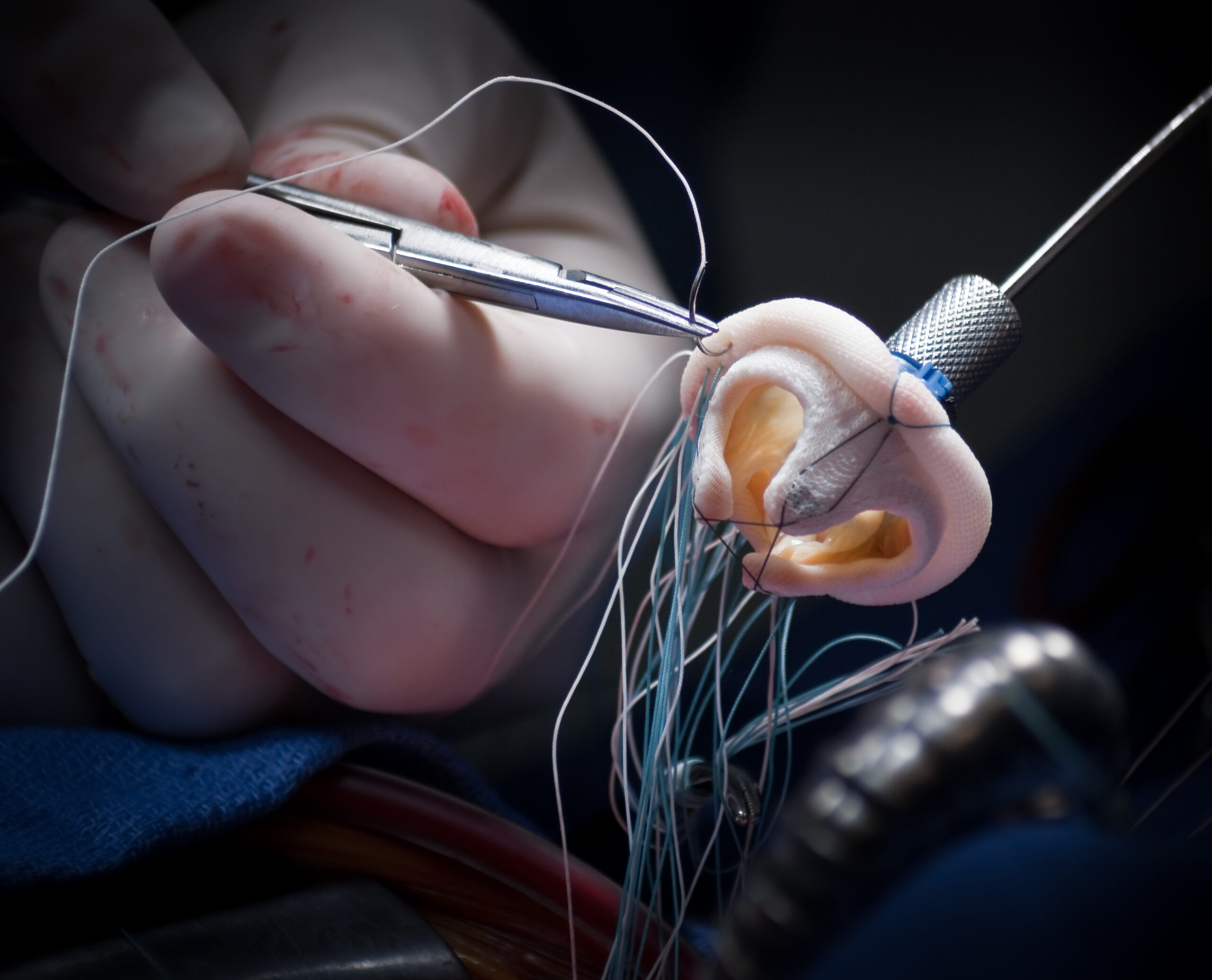
Mitral heart valve
What? Remove oxides, laser pulse marks and heat affected zone (HAZ); Edge rounding at critical locations
Why MicroBlasting? Removes residues effectively and also works to reduce stress concentrations and micro-cracks that can propagate into fracture locations in a polished and implanted device; Also effective at consistent edge rounding within tight tolerances.

Pacemakers
What? Remove cosmetic defects, excess epoxy between the header and the can, metalization on pacemaker connectors, and silicone on pacing leads.
Why MicroBlasting? Provides an effective finishing solution for several different challenges in one tool.
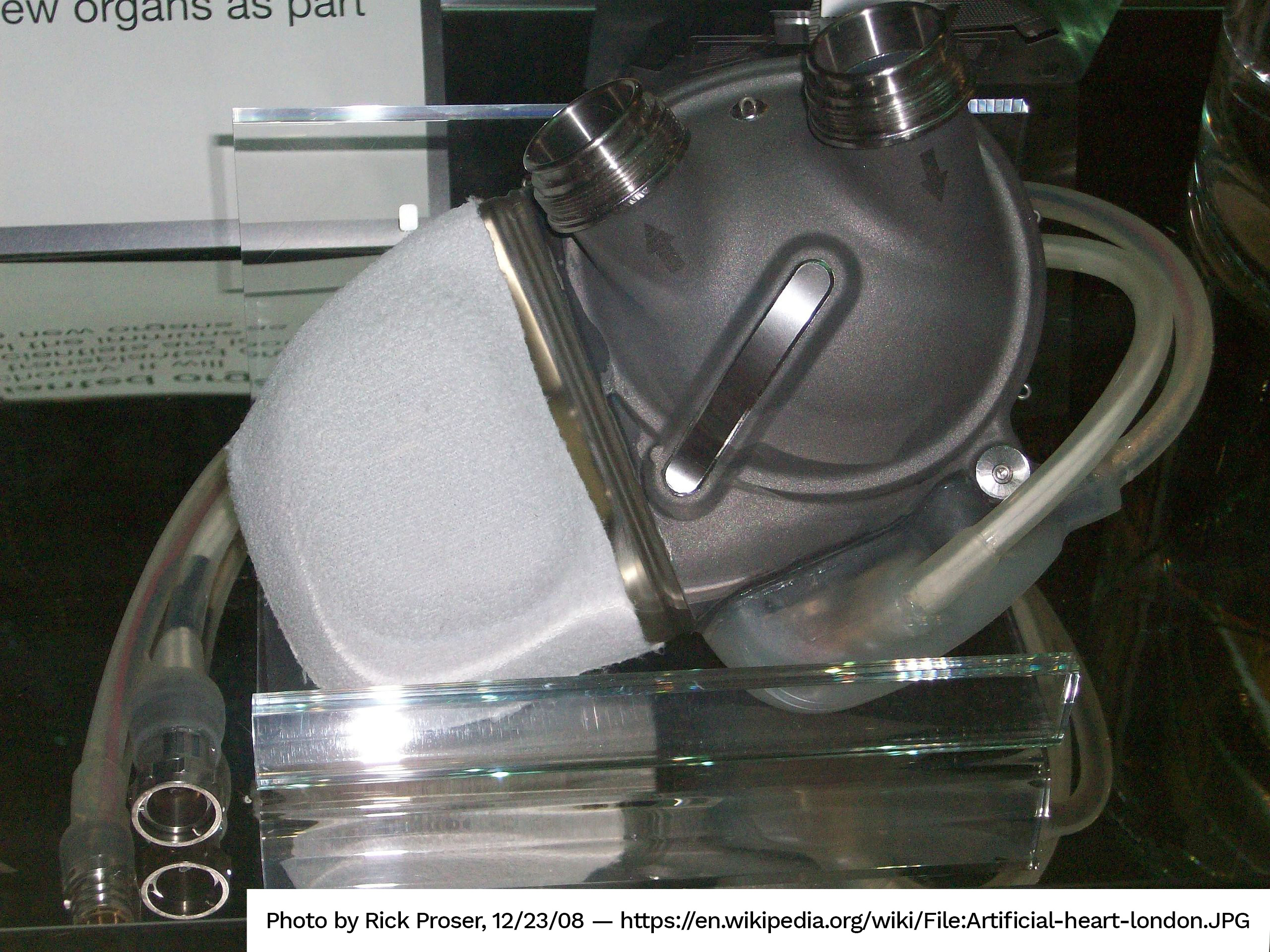

Prosthetic heart
What? Texture for bond adhesion; create surface finish prior to polishing
Why MicroBlasting? Consistently create a specific surface texture.

AAA device
What? Remove oxides, laser pulse marks and heat affected zone (HAZ); Edge rounding at critical locations
Why MicroBlasting? Removes residues effectively and also works to reduce stress concentrations and micro-cracks that can propagate into fracture locations in a polished and implanted device; Also effective at consistent edge rounding within tight tolerances.
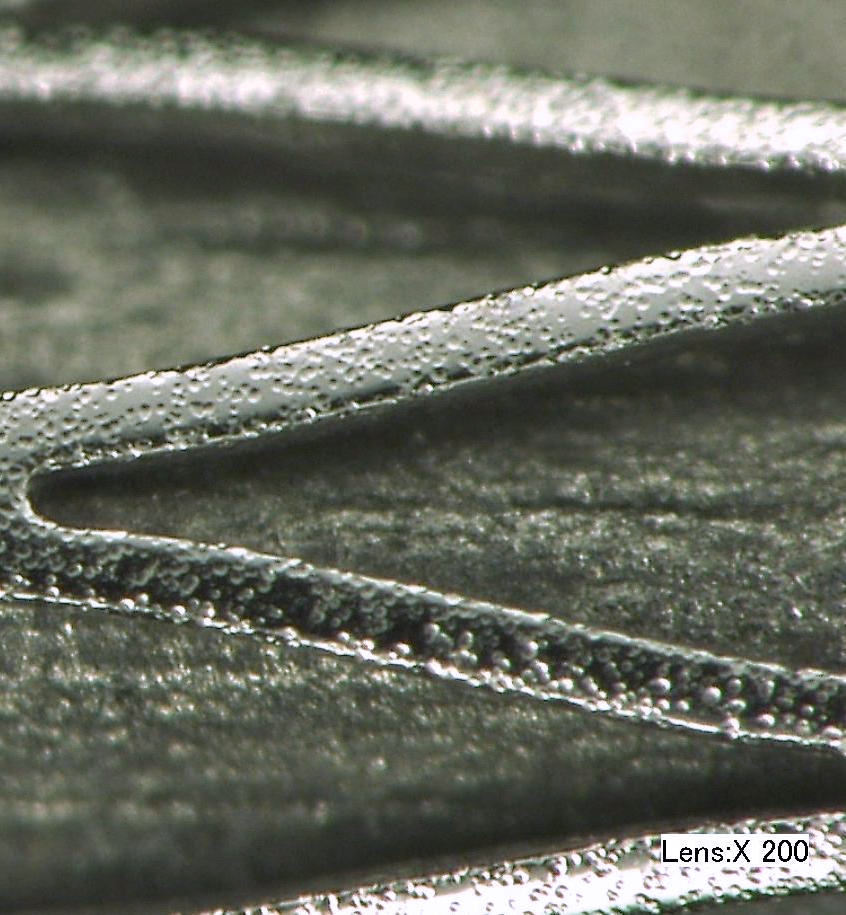
Drug eluting stents
What? Apply a peened surface finish to stainless or cobalt chrome stent
Why MicroBlasting? Control over pocket created is used to meter the medication into the surrounding vessel tissue.
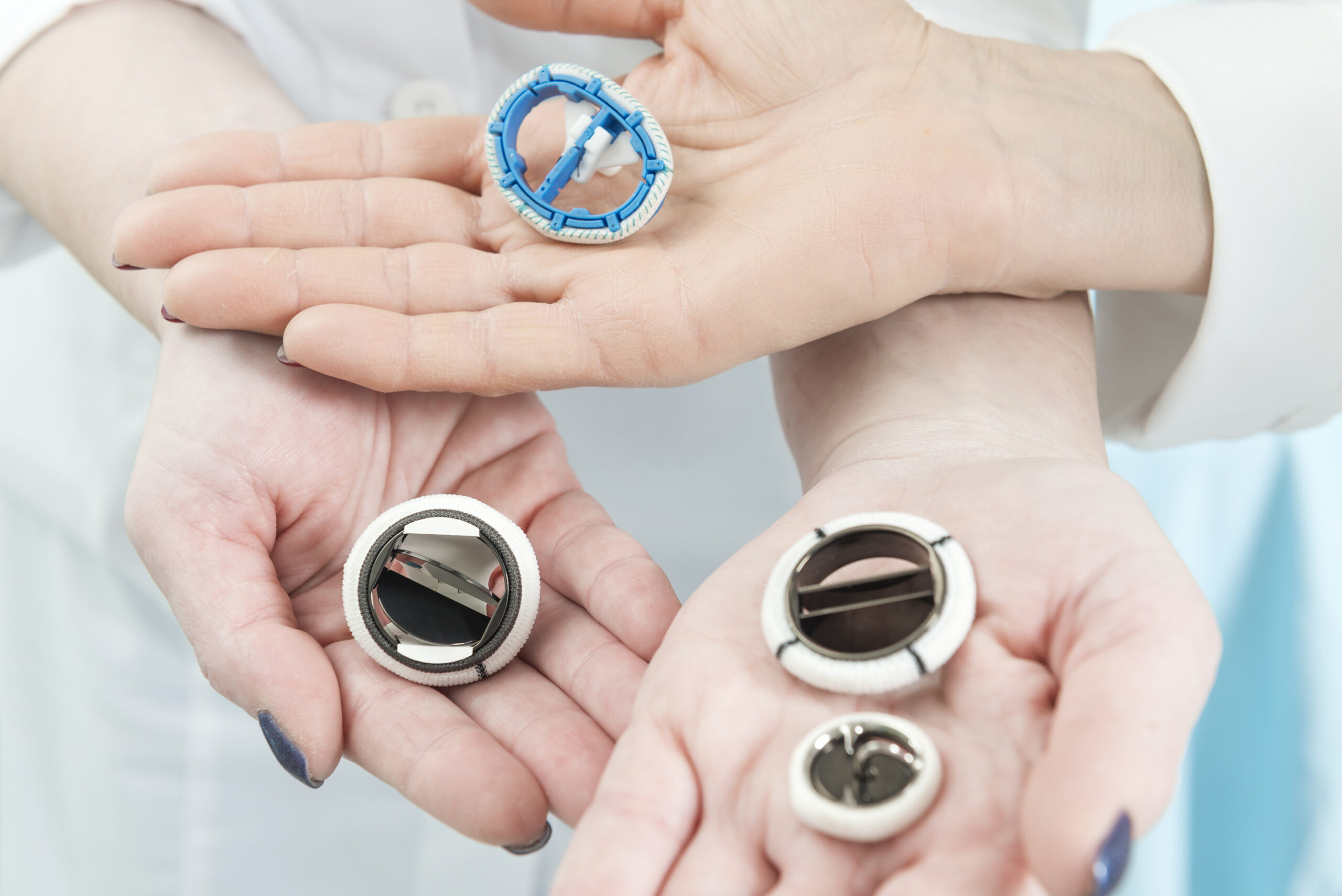

Mechanical heart valve
What? Graphite removal from pyrolytic carbon
Why MicroBlasting? Effectively removes graphite without damaging the carbon.
AED (external defibrillator)
What? Selective conformal coating removal on circuit boards for testing and repair
Why MicroBlasting? Works effectively to selectively remove a variety of coatings
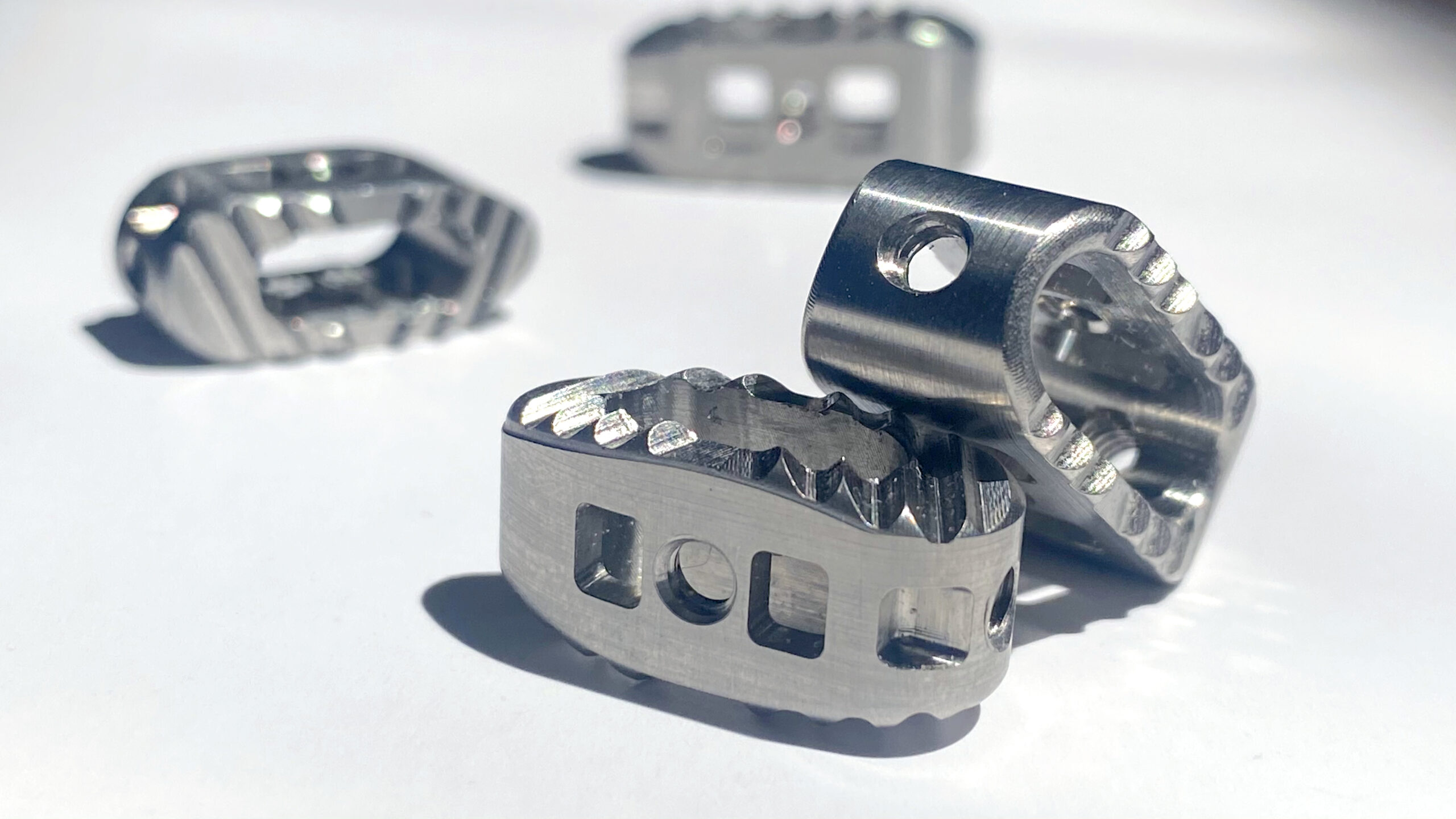

Titanium alloy spinal implants
What? Texture surface and deburr machined or 3D printed parts
Why MicroBlasting? Impart a specific Ra textured finish for improved bone in-growth and remove burrs efficiently without causing dimensional changes.
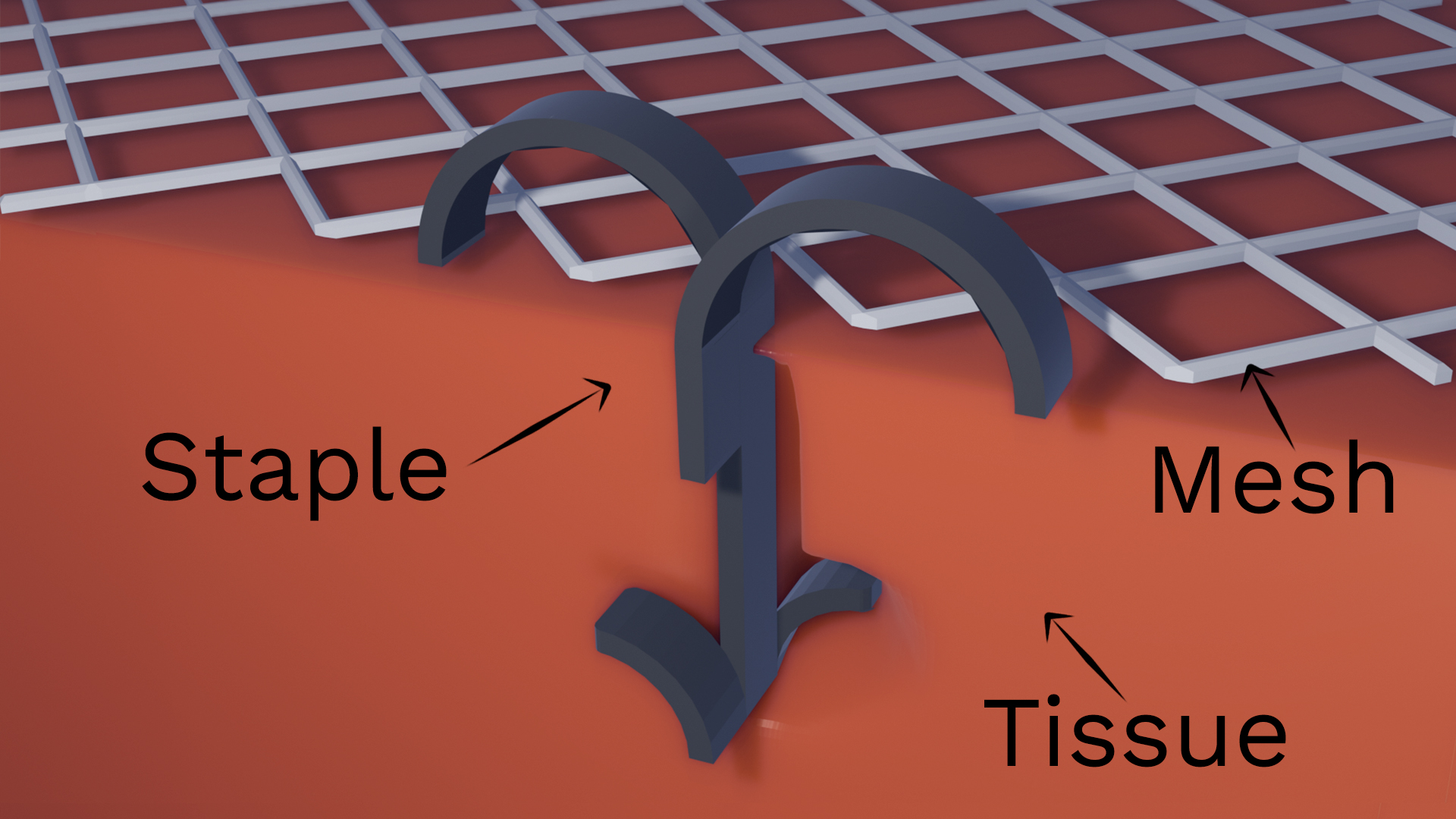
Hernia staples
What? Remove stress concentrations generated from shape setting nitinol; remove oxide and laser pulse marks
Why MicroBlasting? Removing stress concentrations and residues creates a uniform finish that improves the electropolish finish.
Neuro stimulation device – pain management and bladder control
What? Remove cosmetic defects, excess epoxy between the header and the can, metalization on connectors, and silicone on leads.
Why MicroBlasting? Provides an effective finishing solution for several different challenges in one tool.

Bone plates
What? Remove fine burrs left by machining process
Why MicroBlasting? Quickly removes these burrs without altering the surface finish or texture.
Wrist fixation device
What? Remove oxides, laser pulse marks and heat affected zone (HAZ); Edge rounding at critical locations
Why MicroBlasting? Removes residues effectively and also works to reduce stress concentrations and micro-cracks that can propagate into fracture locations in a polished and implanted device; Also effective at consistent edge rounding within tight tolerances.
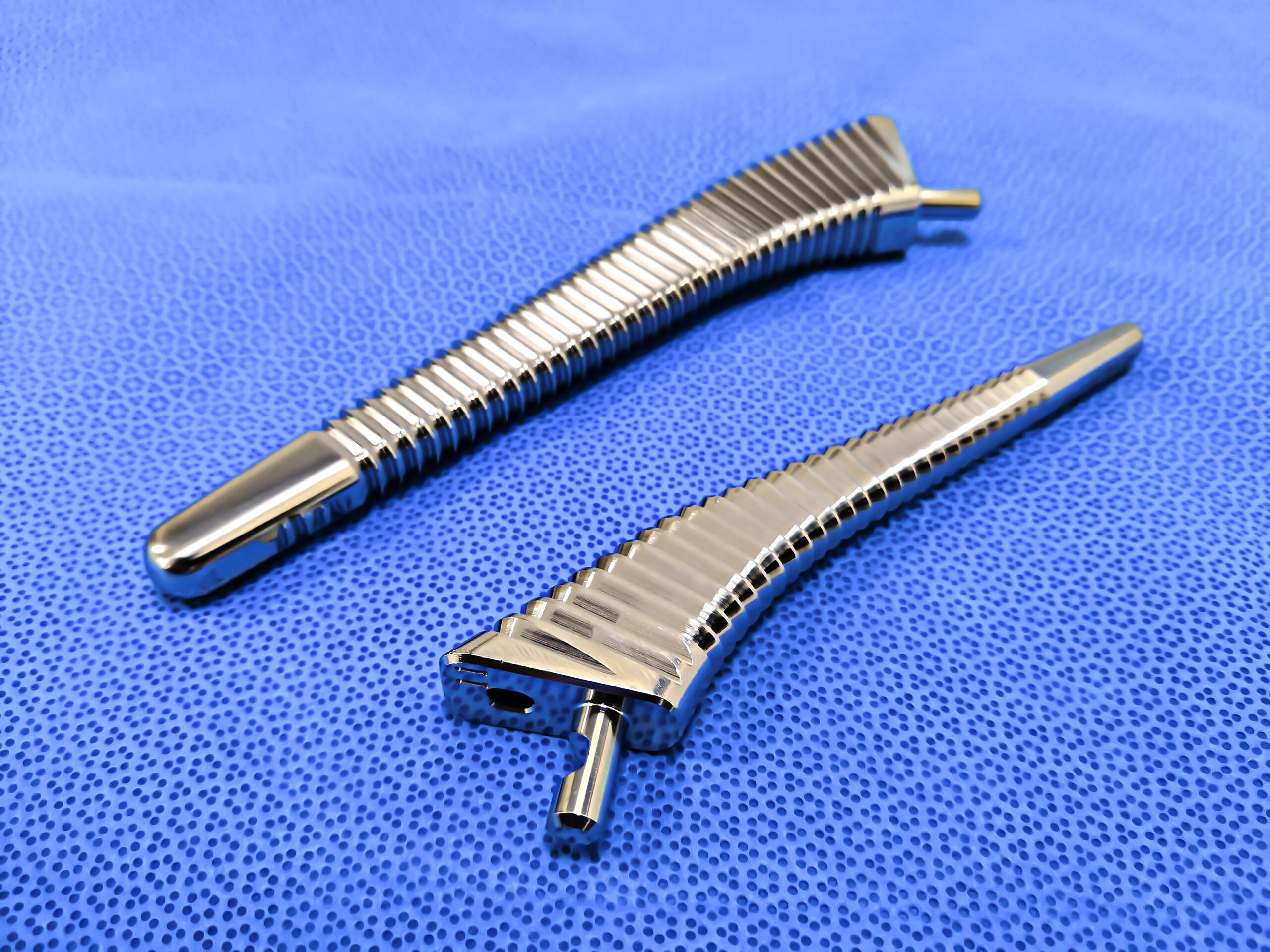

Orthopedic devices
What? Texturing and surface finishing
Why MicroBlasting? Target locations for texturing where the implant needs to be cemented into existing bone; removes machining marks and other imperfections caused by the manufacturing process.
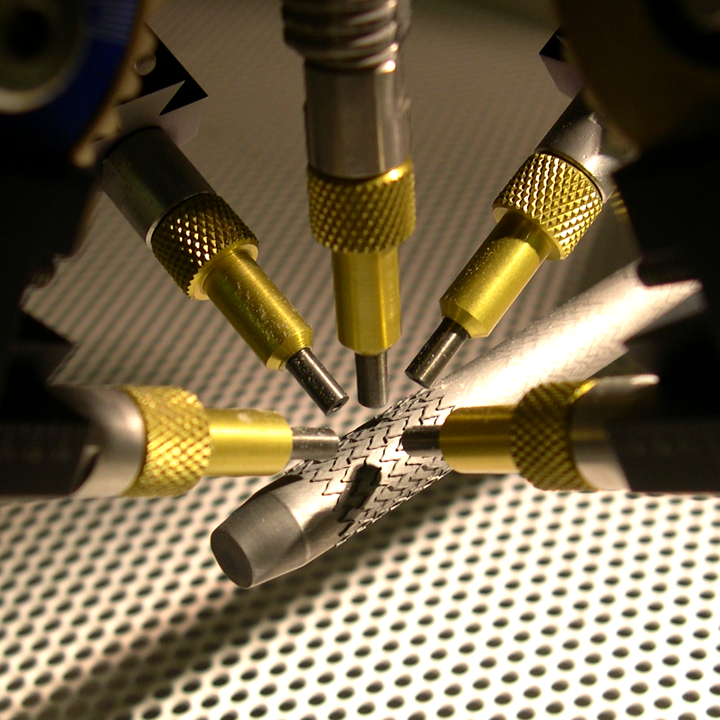
Peripheral stents
What? Remove oxides, laser pulse marks and heat affected zone (HAZ); Edge rounding at critical locations
Why MicroBlasting? Removes residues effectively and also works to reduce stress concentrations and micro-cracks that can propagate into fracture locations in a polished and implanted device; Also effective at consistent edge rounding within tight tolerances.
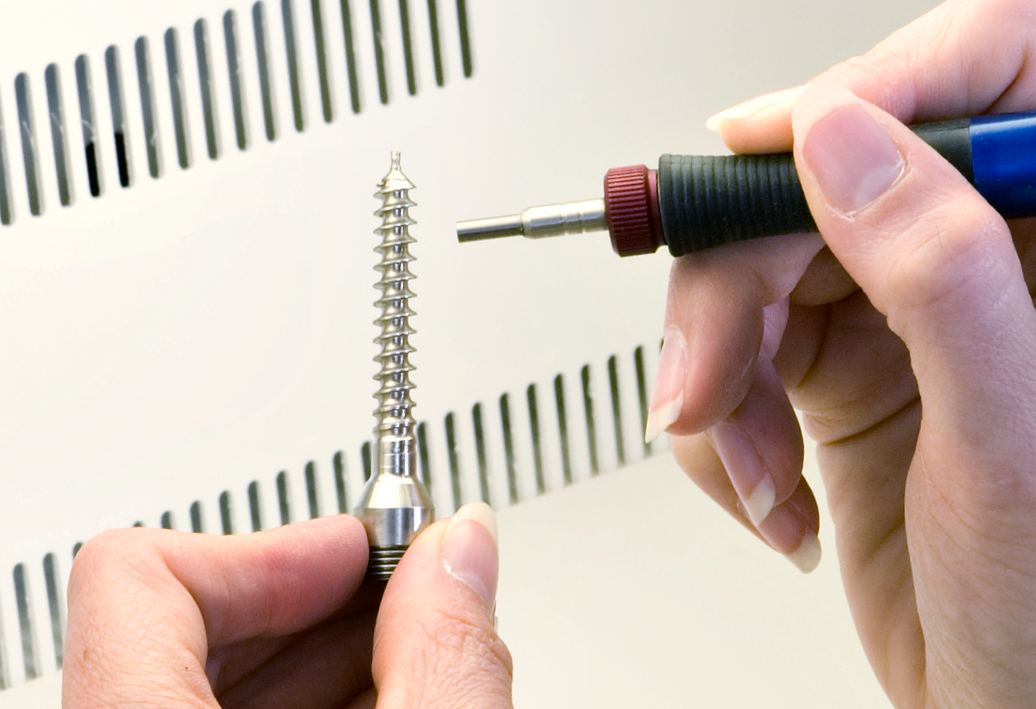

Bone screws
What? Burr removal on threads and socket; texturing screw head
Why MicroBlasting? Efficiently removes burrs without damaging or dulling the cutting edges. Texture to a sharp delineation without masking.
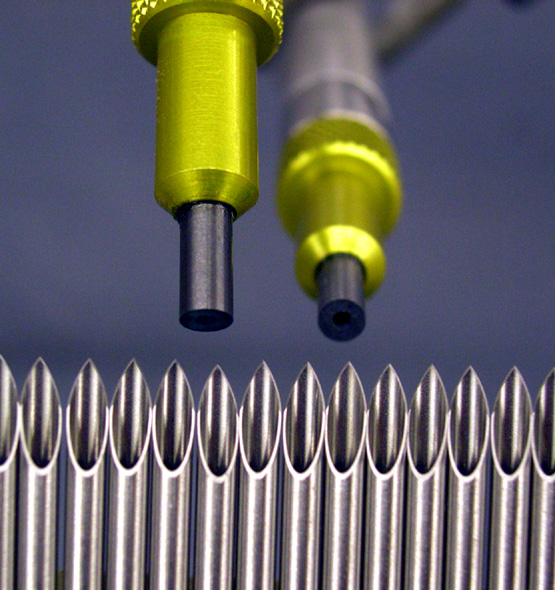
Cannula
What? Remove burr and dull cutting edge at heel; cut side ports holes; deburr side port slots; texture for overmolding bond adhesion
Why MicroBlasting? Ability to target selective areas effectively: targets heel without dulling needlepoint; texture to a sharp delineation without masking.
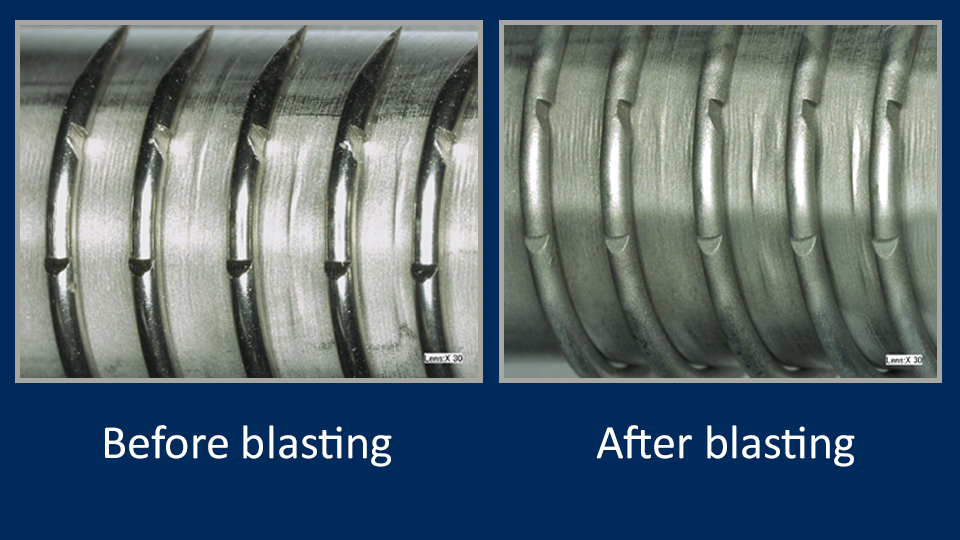
Suture needle
What? Apply a slight radius to the hook to reduce the risk of the suture being nicked during the procedure
Why MicroBlasting? Localized deburring without damaging the part or altering the finish
Guidewires/ Catheters
What? Remove heel burr
Why MicroBlasting? Target heel burr precisely without dulling the cutting tip

PEEK spinal implants
What? – Remove fine feather burrs
Why MicroBlasting? – Operators easily follow the contours of an implant to remove burrs quickly and safely without causing dimensional changes.

Cranial Perforator
What? Deburr blades for drilling cores out of a section in the skull
Why MicroBlasting? Removes burrs effectively without dulling the cutting edge.

Dental Implants
What? – Create a textured surface optimized for osseointegration
Why MicroBlasting? – Achieve a consistent, specific Ra surface finish without reducing major diameter of the threads

Cochlear Implants
What? Deburr miniature components
Why MicroBlasting? Safely removes burrs without causing dimensional changes

3D printed ear parts
What? Strip semi-integrated material from the surface of 3D printed components; create a uniform cosmetic finish
Why MicroBlasting? Removes material without causing dimensional changes

Endoscope
What? Texture for radiopacity
Why MicroBlasting? Efficiently applies a uniform surface finish

Mitral heart valve
What? Remove oxides, laser pulse marks and heat affected zone (HAZ); Edge rounding at critical locations
Why MicroBlasting? Removes residues effectively and also works to reduce stress concentrations and micro-cracks that can propagate into fracture locations in a polished and implanted device; Also effective at consistent edge rounding within tight tolerances.

Pacemakers
What? Remove cosmetic defects, excess epoxy between the header and the can, metalization on pacemaker connectors, and silicone on pacing leads.
Why MicroBlasting? Provides an effective finishing solution for several different challenges in one tool.

Prosthetic heart
What? Texture for bond adhesion; create surface finish prior to polishing
Why MicroBlasting? Consistently create a specific surface texture.

AAA device
What? Remove oxides, laser pulse marks and heat affected zone (HAZ); Edge rounding at critical locations
Why MicroBlasting? Removes residues effectively and also works to reduce stress concentrations and micro-cracks that can propagate into fracture locations in a polished and implanted device; Also effective at consistent edge rounding within tight tolerances.

Drug eluting stents
What? Apply a peened surface finish to stainless or cobalt chrome stent
Why MicroBlasting? Control over pocket created is used to meter the medication into the surrounding vessel tissue.

Mechanical heart valve
What? Graphite removal from pyrolytic carbon
Why MicroBlasting? Effectively removes graphite without damaging the carbon.

AED (external defibrillator)
What? Selective conformal coating removal on circuit boards for testing and repair
Why MicroBlasting? Works effectively to selectively remove a variety of coatings

Titanium alloy spinal implants
What? Texture surface and deburr machined or 3D printed parts
Why MicroBlasting? Impart a specific Ra textured finish for improved bone in-growth and remove burrs efficiently without causing dimensional changes.

Hernia staples
What? Remove stress concentrations generated from shape setting nitinol; remove oxide and laser pulse marks
Why MicroBlasting? Removing stress concentrations and residues creates a uniform finish that improves the electropolish finish.

Neuro stimulation device – pain management and bladder control
What? Remove cosmetic defects, excess epoxy between the header and the can, metalization on connectors, and silicone on leads.
Why MicroBlasting? Provides an effective finishing solution for several different challenges in one tool.

Bone plates
What? Remove fine burrs left by machining process
Why MicroBlasting? Quickly removes these burrs without altering the surface finish or texture.

Wrist fixation device
What? Remove oxides, laser pulse marks and heat affected zone (HAZ); Edge rounding at critical locations
Why MicroBlasting? Removes residues effectively and also works to reduce stress concentrations and micro-cracks that can propagate into fracture locations in a polished and implanted device; Also effective at consistent edge rounding within tight tolerances.

Orthopedic devices
What? Texturing and surface finishing
Why MicroBlasting? Target locations for texturing where the implant needs to be cemented into existing bone; removes machining marks and other imperfections caused by the manufacturing process.

Peripheral stents
What? Remove oxides, laser pulse marks and heat affected zone (HAZ); Edge rounding at critical locations
Why MicroBlasting? Removes residues effectively and also works to reduce stress concentrations and micro-cracks that can propagate into fracture locations in a polished and implanted device; Also effective at consistent edge rounding within tight tolerances.

Bone screws
What? Burr removal on threads and socket; texturing screw head
Why MicroBlasting? Efficiently removes burrs without damaging or dulling the cutting edges. Texture to a sharp delineation without masking.

Cannula
What? Remove burr and dull cutting edge at heel; cut side ports holes; deburr side port slots; texture for overmolding bond adhesion
Why MicroBlasting? Ability to target selective areas effectively: targets heel without dulling needlepoint; texture to a sharp delineation without masking.

Suture needle
What? Apply a slight radius to the hook to reduce the risk of the suture being nicked during the procedure
Why MicroBlasting? Localized deburring without damaging the part or altering the finish

Guidewires/ Catheters
What? Remove heel burr
Why MicroBlasting? Target heel burr precisely without dulling the cutting tip
55 +
years
We have over 55 years of experience in perfecting MicroBlasting technologies and partnering with clients to help them solve their unique manufacturing challenges.
1000+
customers serving the medical device industry
From job shops to top tier medical device manufacturers, we have worked with a wide range of medical device designers and manufacturers to improve their processes. Whether you’re looking to solve a problem in-house or provide a solution to your contract manufacturing partner, we’re ready to work with you.
175+
automated systems in 20+ countries worldwide
From North America to Europe to Asia and on to Africa and South America, Comco has traversed the globe to install custom automated microblasting solutions to far reaching customers.
Your Partner for Industrial Engineering Solutions
We’ll work closely with you by applying our engineering skills to your problem, providing the process with our technologies, and sharing our accumulated expertise to develop solutions that are efficient and cost effective.
-
Applied Engineering with a Deep Understanding of Medical Parts
Engineering is at the core of Comco. Our engineers have a background in the medical, aerospace, and semiconductor industries. While we are experts at MicroBlasting, we can also “speak your language.”
-
Providing the process at no additional cost to you
Let us prove how a custom MicroBlasting process would work for you while sharing our engineering expertise up front, without charge.
-
Sharing our skills & knowledge throughout our partnership
We’ll share our engineering skills and knowledge at every step of our partnership. Advanced technical support continues beyond your initial purchase of our MicroBlasting systems, and we also offer assistance with new applications as they arise.
What can be achieved with MicroBlasting?
Whether it’s deburring bone screws, needle or implant, removing dross from laser cut stents or imparting an aesthetic surface finish on pacemaker cans, MicroBlasting technology has a wide range of uses in the medical device industry.
Four Processes, Countless Applications
Select a MicroBlasting process below to see examples of related medical manufacturing solutions
Dental Implants
Bone Screws
Surface Texturing on the Blog
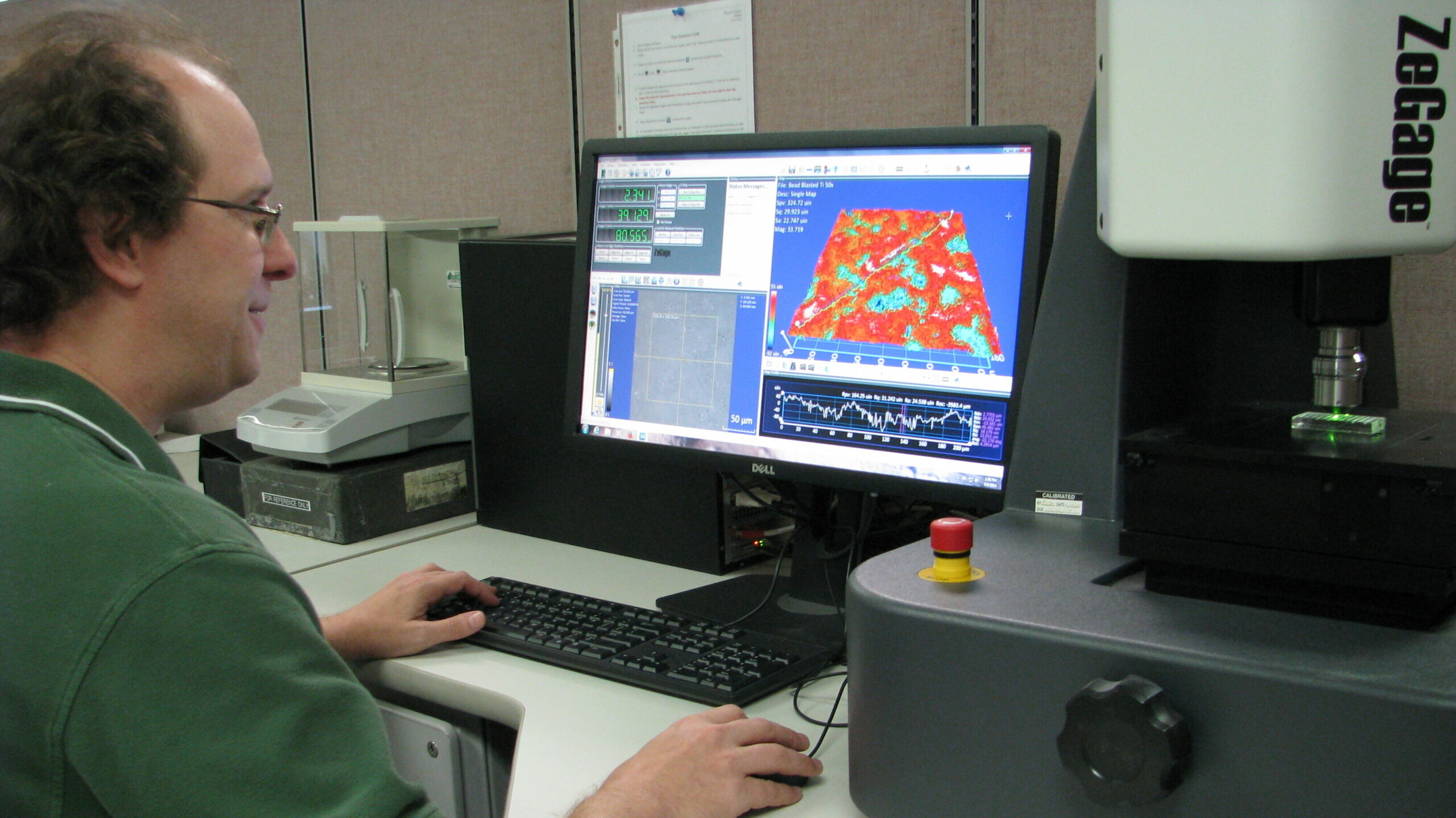
Need a consistent and repeatable surface finish?
Not getting a consistent surface finish? Change your surface finish spec to include three measurable details. Learn what your spec may be missing, and why these three points yield repeatable returns.
Read More
How to calculate stepover and get a uniform surface finish
Avoid uneven results while texturing or etching parts. Learn what stepover percentage works in most applications. Incl. stepover calculator.
Read More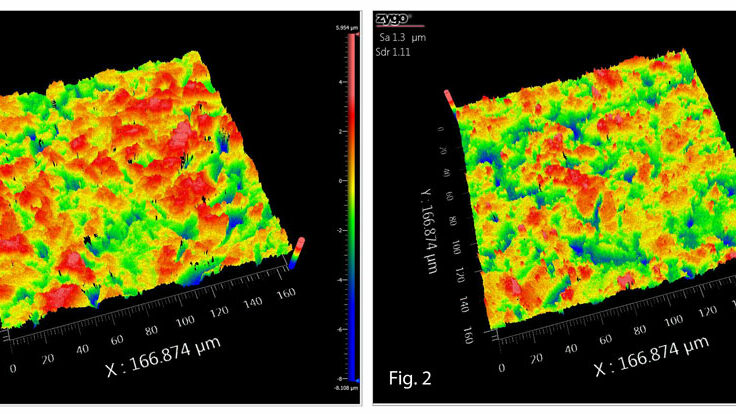
Need to Improve Bond Strength?
Ra or Sa alone cannot predict bond strength in all applications. Epoxied surfaces, in particular, require a more comprehensive specification. To get repeatable results in pull and peel tests, incorporate a high developed surface ratio (Sdr) and require full coverage.
Read MoreNitinol Stents
Pacemakers
Selective Cleaning on the Blog
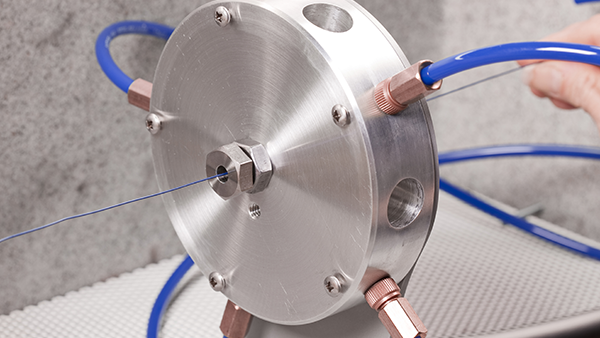
Wire stripping? Get uniform removal + sharp delineation with the ring nozzle
A selection of micro-lessons from our blog that focus on advances in MicroBlasting tools and technology. Includes design and development of new equipment and accessories to help you blast better.
Read More
Conformal Coating Removal
Wheat starch is a very soft abrasive, but it has just enough abrading power to gently lift really thin layers of conformal coating without risk to an underlying solder mask or circuit board. Learn why you may want to consider it, and learn why MicroBlasting, in general, is a great method for conformal coating removal.
Read MorePEEK Spinal Implants
Bone Screws
Precision Deburring on the Blog

5 Factors that Lead to Successful Deburring
In this quick video lesson, we break down the 5 factors that impact most deburring applications. When you’re done, you’ll know how to deburr…better!
Read More
Six Quick Deburring Case Studies
Learn what abrasive, nozzle and blast pressure are used to precisely remove burrs and refine surfaces on these small, intricate parts. Includes: metal gears, PEEK spinal implants, electronic packages, stainless steel valve components, aluminum fixtures and titanium components.
Read More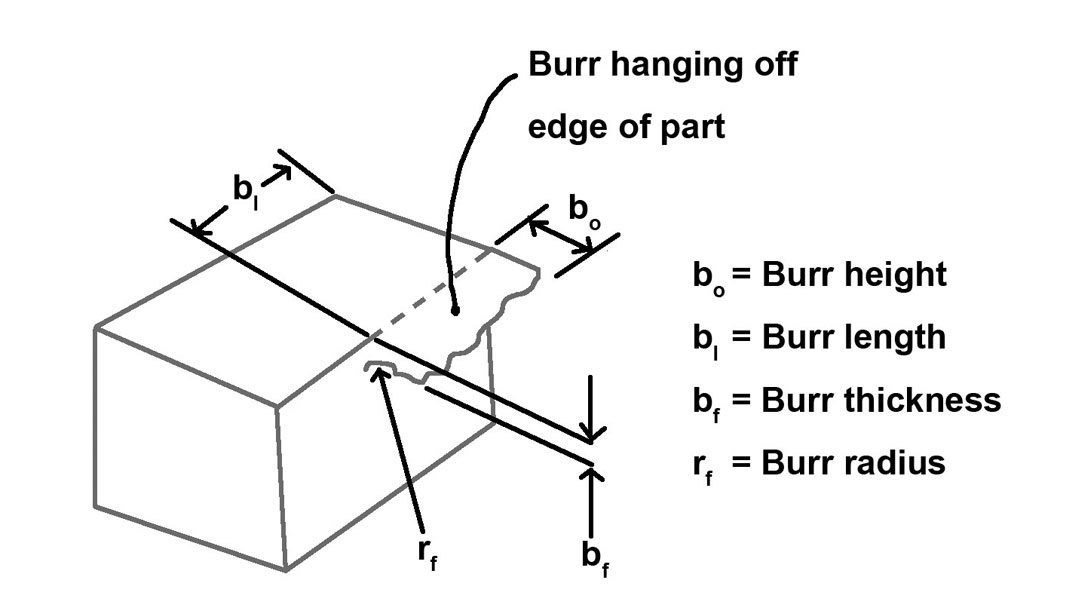
The Missing Measurment of Deburring
Are old burrs suddenly reappearing? Are burrs popping up in a new location on your part? Is a once-reliable deburring method starting to fail? Chances are, you’re missing a measurement. Manufacturing expert, LaRoux Gillespie, shares the deburring measurements often missed that lead to recurring problems and new burr formations.
Read MoreMechanical Heart Valves
MicroFluidics
Abrasive Jet Machining on the Blog
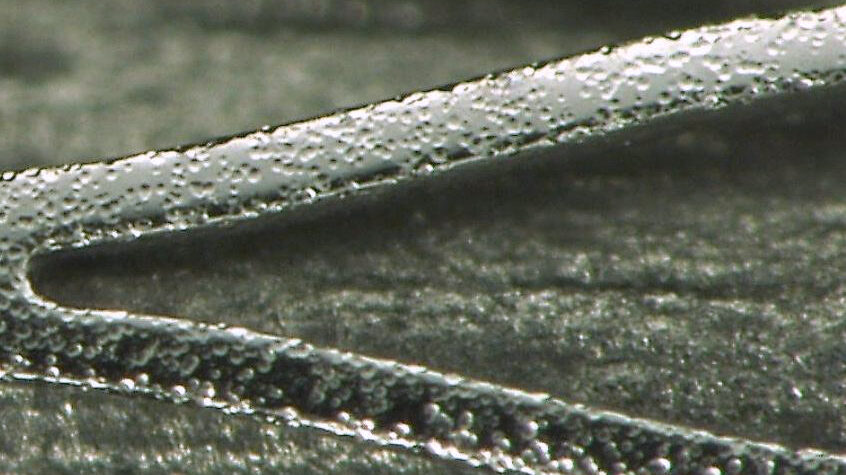
Edge rounding on Nitinol implants
Aluminum oxide has long been the go-to abrasive for cleaning stents, valves, and other Nitinol implants before electropolishing. But recently, selective edge-rounding entered the application, and aluminum oxide was not enough. This month, we look at how glass bead took a radius from 2 microns to 24 microns.
Read more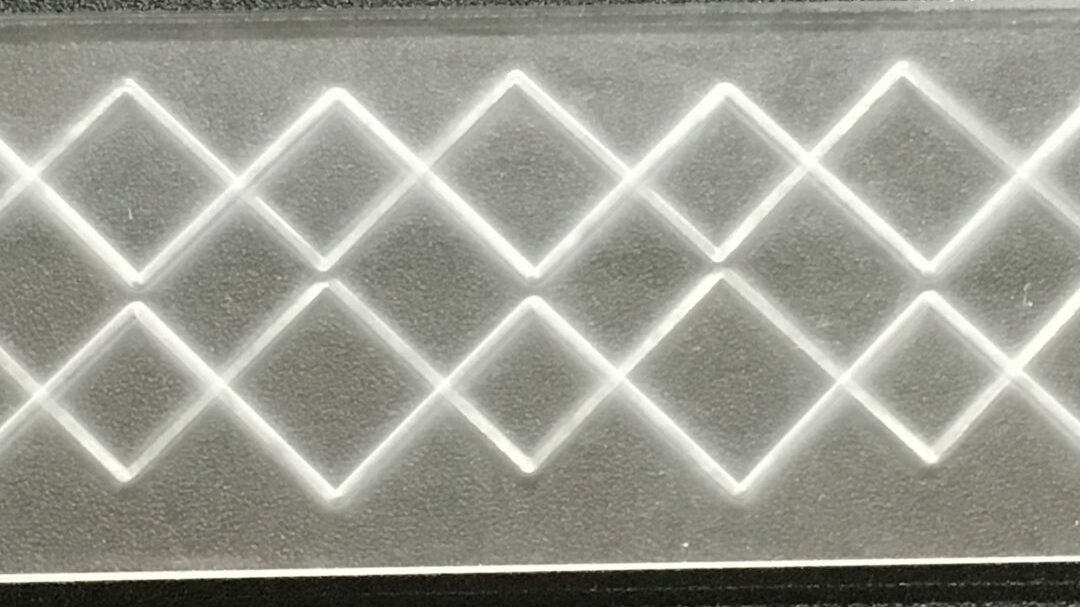
How to reliably create features to
A single pass of the focused abrasive stream from a MicroBlaster can uniformly remove 5 µin (0.127 microns) or less of material depending on the substrate, abrasive, and blast parameters. Given this level of precise and controllable erosion, you simply need to know how to fine-tune the process to suit your application.
Read more
5 variables for abrasive jet machining
Using MicroBlasting to cut or etch a part (a process also known as controlled erosion) is a great method to machine many precision parts, from drilling holes in ceramic substrates to cutting slots in fragile silicon and glass wafers.
Read moreReady to get started with MicroBlasting?
Contact UsMaterials: What you’re working with
MicroBlasting is an effective process for a variety of materials and compositions. Click below to view and search materials we often work with that are used by the medical industry.
Browse Materials
Materials We’ve Worked With
MicroBlasting is used on a variety of materials and compositions, thanks in part to the wide range of abrasive media available. We often work with the following materials used by the medical industry.
Can’t find what you’re looking for? Contact us and we’ll let you know how your material(s) can be used with our MicroBlasting technologies.

Aluminum

Bronze

Copper

Ceramic

Glass

Graphite

Inconel

Kovar

Nitinol

Polypropylene

PEEK

PTFE
Silicon

Stainless Steel

Titanium

Brass
A Complete MicroBlasting Solution
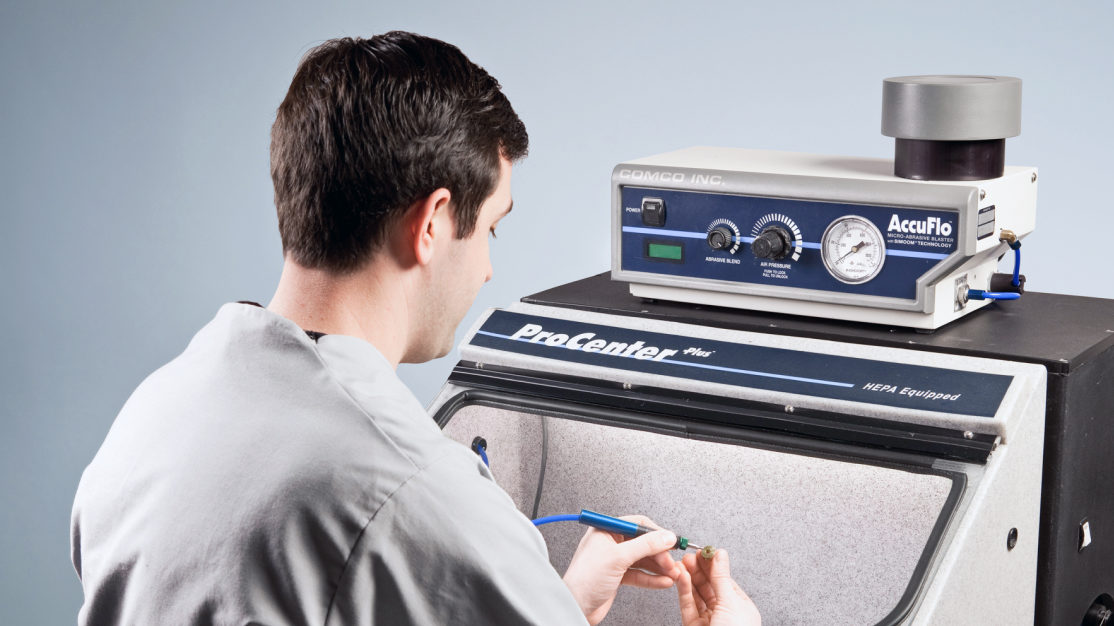
Whether you need a manual or automated workflow for your application, we’ve got you covered. Our MicroBlasting systems are precise, easy to configure for repeatable processes, and produce, clean, consistent results with each use
Benefits of the Manual System
Comfortable
Ergonomic design reduces operator fatigue
Versatile
Flows a wide range of media
Consistent
Unique patented modulated abrasive feed
User Friendly
Easy to set-up and easy to maintain
Mobile
Casters allow for adaptive cell environments.
Clean and Quiet
Hepa filtration and customized fan box improves operation.
Cost-Effective
Our best deal for a turnkey solution
Benefits of the Automated System
Customizable
Offers a range of workholding and blast head options
Scaleable
Designed to grow from manual to fully automatic
User friendly
Intuitive user interface for programming and operation
Turnkey
Delivered production ready
Peace of mind
Fully documented and supported
Consistent
Unique patented modulated abrasive feed
Robust
Stable in Full Production
Your Privacy & Security Are Our Priority
-
Our Commitment to Privacy
We are committed to protecting our clients. That’s why we take your highly specialized, confidential projects seriously.
-
Trusted Partners
Great customer relationships begin with trust. We are dedicated to protecting our clients’ confidential R&D sample parts and data.
-
Learn More
Contact us to learn more about how we follow the highest standards to protect your business data.
Send us your sample Part!
MicroBlasting’s benefits can be a bit of a mystery. Our applications engineers have the experience and complete test facilities to process your parts. If you think MicroBlasting may be appropriate for your application, our team would love the opportunity to help you out.